Jaundice Symptoms, Causes & Treatments
What is Jaundice?
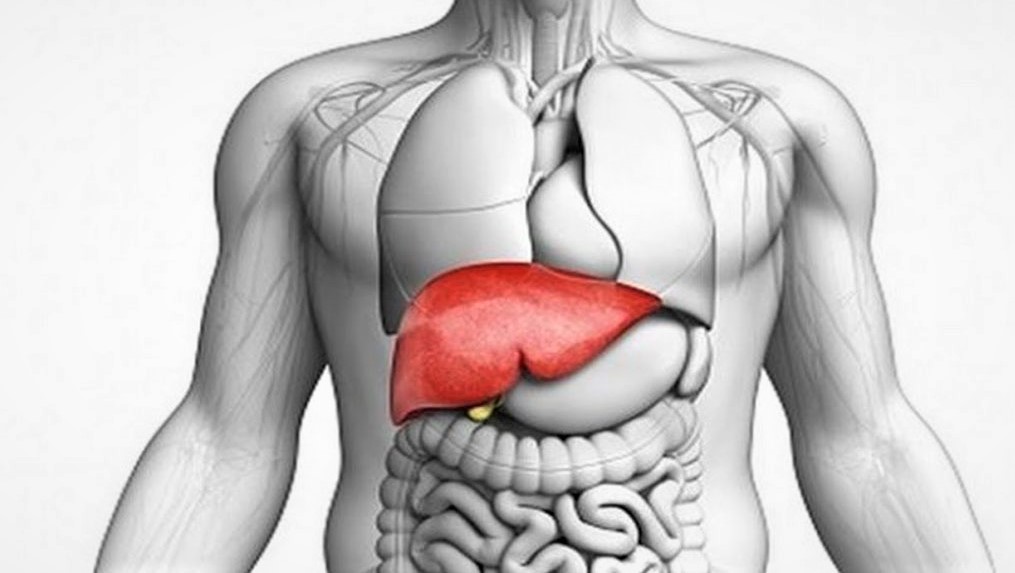
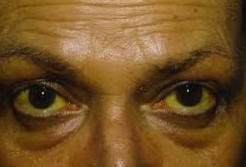
Jaundice is a disease which causes yellow discolouration of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes caused for an increased level of bilirubin in the blood. Jaundice is also known as Icterus.
What is Bilirubin & what is the Normal Level?
Bilirubin is formed by the daily natural breakdown of red blood cells in the body & the liver helps to excrete it in the form of bile. Bilirubin is brown and yellow in colour, and it is this pigment that makes faeces brown. Levels of bilirubin in blood are normally below 1.0 mg/dL (17 µmol/L) and levels over 2–3 mg/dL (34-51 µmol/L) typically results in jaundice. The skin normally becomes yellow once levels reach between 2 and 3 mg/dL. Jaundice Symptoms is seen when at High bilirubin level.
High bilirubin is divided into two types: 1) Conjugated- This means it is water-soluble and can be excreted. 2) Unconjugated- It is water-non soluble, can’t be removed from the body. Unconjugated bilirubin is toxic, but conjugated bilirubin is usually not. Conjugated bilirubin can be confirmed by finding bilirubin in the urine.
What Causes Jaundice?
Jaundice may be caused for different reasons.
Pre-hepatic:
Pre-hepatic jaundice is caused by anything that causes an increased rate of hemolysis (breakdown and destruction of red blood cells).
Examples with increased breakdown of red blood cells include:
- Malaria,
- Sickle cell crisis,
- Thalassemia,
- Autoimmune disorders,
- Spherocytosis,
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD),
- Pyruvate kinase deficiency,
- Drugs or other toxins.
Hepatocellular (the problem arises within the liver):
Jaundice in these cases is caused by the liver’s inability to properly metabolize and excrete bilirubin. Examples include:
- Hepatitis (commonly viral or alcohol related),
- Hepatotoxicity
- Liver cirrhosis,
- Drugs or other toxins,
- Gilbert’s syndrome
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome,
Post-hepatic:
Jaundice in these cases, also termed obstructive jaundice, is caused by conditions which interrupt the normal drainage of conjugated bilirubin in the form of bile from the liver into the intestines.
Example:
- Gallstones in the bile ducts,
- Cancer (pancreatic and gallbladder/bile duct carcinoma),
- Pancreatic pseudocysts,
- Strictures of the bile ducts,
- Pancreatitis,
- Parasites,
- Cholangitis,
- Congenital malformations,
Neonatal & newborn jaundice:
Neonatal jaundice is usually harmless: this condition is often seen in infants around the second day after birth, lasting until day 8 in normal births, or to around day 14 in premature births. It can also be for other reasons, examples:
- ABO/Rh blood type autoantibodies
- Hereditary spherocytosis,
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency,
- Breast milk jaundice
- Breastfeeding jaundice
- Cephalohematoma
Jaundice Symptoms:
Common signs and symptoms seen in individuals with jaundice symptoms include:
- Yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes,
- Light-colored stools,
- Dark-color urine,
- Itching of the skin.
The underlying disease process may result in additional signs and symptoms. These may include:
- Nausea and vomiting,
- High or low fever,
- Abdominal pain,
- Weakness,
- Loss of appetite,
- Headache,
- Confusion,
- Swelling of the legs and abdomen.
Investigation & Diagnosis of Jaundice:
Investigation & Diagnostic test will be needed upon the patients conditions. Know about different options:
- A blood test is usually performed to confirm the diagnosis of jaundice, which includes bilirubin tests, full blood count of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, and Hepatitis A, B, and C tests.
- Blood tests- complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests (including a bilirubin level), lipase/amylase level to detect inflammation of the pancreas.
- Urinalysis
- Imaging Studies- Ultra sound, CT, MRI etc.
- Liver Biopsy
What are the treatment options of Jaundice?
Treatment depends on the cause of the underlying condition leading to jaundice and any potential complications related to it.
- Hepatocellular jaundice is treated with antibiotic medications and steroids
- Hemolytic jaundice is treated with iron supplements, sometimes intravenous fluids, medications & blood transfusions may be required
- Obstructive jaundice is treated with surgery to remove the obstruction followed by medication
- There is also medication-induced jaundice in such cases the medicines are discontinued and alternative medicines are prescribed.
For infants with jaundice the treatments include:
- Phototherapy
- Blood transfusion
Self-Care at Home for Jaundice:
The objectives of home care helps symptom relief and improve the medical condition. The various measures that may be undertaken include:
- Maintain adequate hydration by drinking fluids,
- Complete rest is needed.
- Take medications only as instructed and prescribed by a health care practitioner.
- Avoid medications, herbs, or supplements which may cause detrimental side effects. Consult a health care practitioner for advice.
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Certain dietary restrictions, avoid oily food may be recommended by a health care practitioner.
- In certain cases of newborn jaundice, the parents or caregivers can place the baby next to a well lit window a few times a day to decrease elevated bilirubin levels. In more severe cases, a health care practitioner may need to discharge the baby home from the hospital with home phototherapy.
- Provide adequate milk intake for the baby in cases of breastfeeding jaundice.
- If any times symptoms worsen or if any new symptoms arise, don’t neglect it consult a health care practitioner.

0 Comments