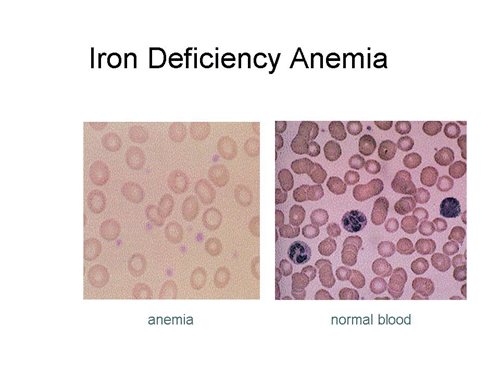
Iron deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is common types of anemia caused for an insufficient of iron in the body. Iron is very important in maintaining many body functions, without enough iron the body can’t produce enough of blood component hemoglobin in red blood cells that enables them to carry oxygen as a result, iron deficiency anemia. Iron is a very important substance of haemoglobin.
What is Anemia?
It is a health condition in which the number of Red Blood Cell (RBC) counts or Hemoglobin (Hb) is low than the normal level. Anemia or Anemia is caused by either a decrease in the production of red blood cells or hemoglobin or for the destruction of red blood cells or loss (usually due to excessive blood loss). The normal range for hemoglobin may differ between the sexes and is approximately 13 to 18 grams per deciliter for men and 12 to 16 grams per deciliter for women.
Sign & Symptoms of iron deficiency Anemia:
The symptoms of moderate to severe iron deficiency anemia include:
- Fatigue & weakness
- Dizziness
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath & irregular heartbeat
- Tingling or crawling feeling in the legs
- Tongue swelling or soreness
- Cold hands and feet
- Brittle nails
- Headaches
Causes of Iron deficiency anemia:
Iron deficiency anemia relates directly to a lack of iron in the body. Know about all causes:
- Inadequate iron intake: The body regularly gets iron from the daily foods you eat. If you consume too little iron in his/her diet over time your body can become iron deficient. Examples of iron-rich foods include meat, eggs, poultry, seafood, nuts, beans, leafy green vegetables and iron-fortified foods.
- Blood loss: Accidental blood loss or menstruation blood loss or body any internal bleeding etc.
- An inability to absorb iron: Iron from food is absorbed into your bloodstream in your small intestine. An intestinal disorder or surgeries, such as celiac disease, or intestinal surgery such as gastric bypass which affects your intestine’s ability to absorb nutrients from digested food, can lead to iron deficiency anemia.
- Pregnancy: Low iron levels are a common problem for pregnant women. The growing fetus needs a lot of iron, which can lead to an iron deficiency.
- Parasitic disease caused by infestation with parasitic worms (helminths); specifically, hookworms, which include Ancylostoma duodenale, Ancylostoma ceylanicum, and Necator americanus, are most commonly responsible for causing iron-deficiency anemia
Risk factors of Iron deficiency anemia:
Anemia is a common condition and can occur in both men and women of any age and from any ethnic group. Some people may be at greater risk, including:
- Women lose blood during menstruation, women in general are at greater risk of iron deficiency anemia.
- Pregnant women
- People with improper diets
- Vegetarians who don’t replace meat with another iron-rich food
- People who donate blood frequently
- Infants and children, especially those born prematurely or experiencing a growth spurt
Prevention:
Choose iron-rich foods include:
- Red meat, pork and poultry
- Beans & spinach
- Seafood
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Dried fruit, such as raisins and apricots
- Iron-fortified cereals, breads and pastas
- Peas
Choose foods containing vitamin C to enhance iron absorption
Vitamin C is also found in:
- Broccoli
- Grapefruit
- Oranges
- Kiwi
- Strawberries
- Melons
- Tomatoes
- Tangerines etc.
Preventing iron deficiency anemia in infants: feed your baby breast milk or iron-fortified formula
Diagnosis:
- Blood tests for iron deficiency anaemia- It includes routine blood tests, haemoglobin, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular haemoglobin, hematocrit value
- The iron level in your blood
- Ferritin levels & serum iron-binding protein levels
- Total iron-binding capacity (TIBC)
Treatment and self-management: Iron deficiency anemia is usually treated in two ways, which involve increasing iron intake and treating any underlying conditions.
- After doctor advice iron supplements to help correct iron intake levels. Note: improper too much iron can be toxic and damage the liver, take iron supplements on doctors’ advice.
- If an underlying condition is found, further treatment may be needed.
- A doctor may prescribe birth control pills to women who have heavy periods. This can reduce the amount of menstrual bleeding each month.
- Self-management involves adding more iron and vitamin C to the diet & take proper diet.

0 Comments